- Home /
- Technical Resources /
- Electroporation Education
Electroporation Education
Explore this section to learn about the many applications for electroporation and electrofusion. BTX generally recommends a system that has an exponential decay waveform for bacteria, plant cells, insect cells, and yeast applications, and a square waveform for mammalian cell work.
Table of Contents
- 1. What is Electroporation?
- 2. Electroporation Applications
- a. Bacteria and Yeast
- b. Plants and Insects
- c. Mammalian Cell Transfections
- d. In Vivo, In Utero and In Ovo Applications
- 3. Electroporation Guides
- a. Systems Crossover Guide
- b. Decisions Guide
- c. Definitions Guide
- d. General Optimization Guide
- 4. BTX Electroporation Systems
- 5. Electroporation Bibliography
- a. In Vitro Electroporation
- b. In Vivo Electroporation
- c. In Utero Electroporation
- d. Ex Vivo Electroporation
- e. Electrofusion
- f. Microinjection
1. What is Electroporation?
Electroporation has become the research standard for the introduction of biological material into cells.
Electroporation is the application of controlled electrical pulses to living cells in order to permeabilize the cell membrane for the purposes of transfection or transformation. These pulses are delivered to a pair of electrodes by a pulse generator. The pulse induces a transmembrane potential which causes the reversible breakdown of the cellular membrane. This action results in the formation of pores that allow molecules, such as DNA, proteins or antibodies, to enter the cell. The process involves two variables, field strength and pulse length. These variables are manipulated in order to maximize the efficiency of gene transfer. A third variable, pulse shape, is dependent upon the type of pulse generator used. Below, we have included an Optimization Guide to help you achieve the best results. Due to it’s ease of use, reproducibility, high efficiency and low toxicity, electroporation has become the method of choice for introducing many types of molecules into cells such as mammalian, bacterial, yeast, plant and insect.
2. Electroporation Applications
Bacteria & Yeast
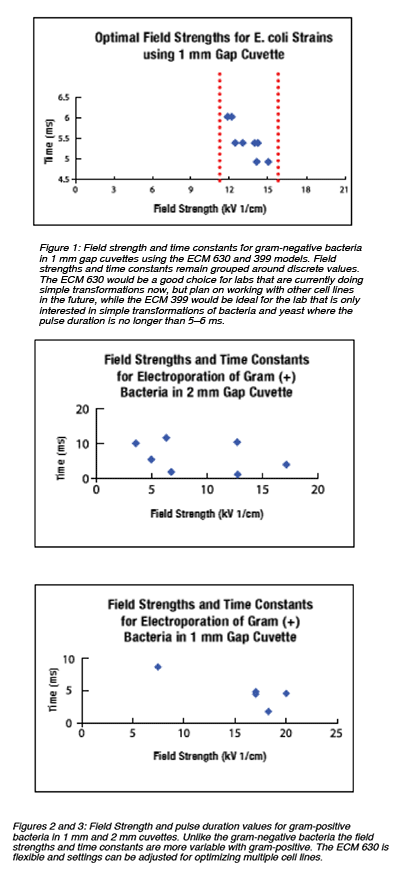
Electroporation is recognized as one of the most efficient methods of transforming human genes into prokaryotic cell lines. Researchers use this technique to express recombinant proteins to study gene function and for the therapeutic treatment of human diseases. Typically, the most commonly transformed cell lines are bacteria and yeast, such as Escheria coli, Agrobacterium Tumerfaciens, Pichia pastoris and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Electroporation of these gram-negative bacterial strains can achieve transformation success rates in the range of 1X1010 transformants/µg DNA. Gram-positive bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Lactobacillus strains present more of a challenge in achieving transformation success due to their cell wall composition. Electroporation as a technique is able to achieve exceptional results in gram-positive strains in the range of 1X107 to 1X1010 transformants/µg DNA.
Other more difficult or less utilized prokaryotic cell lines have also achieved significant positive transformation results with this method. These cell lines include anaerobic bacteria such as Desulfovibro vulgaris, Dictyosteliidium, a celluar slime mold, proprietary modified bacteria lines produced for biofuels, mycoplasma, bacillus genera and parasites such as Leishmania.
Electrical transformation has proven to be highly efficient and easily performed in single cuvettes or multi-well electroporation plates (25- or 96-well options) for greater sample quantities.
High Field Strength
High field strengths (voltage applied between electrode gap measured as kV/cm) are critical to achieve high efficiency transformations in prokaryotic cell lines. The ECM 399, ECM 630 and Gemini can attain the optimal voltage ranges up to 2500 V to provide field strengths of 12 to 25 kV/cm which are essential for prokaryotic applications.
Optimized Time Constants
The time constant or pulse duration is a crucial factor in achieving high efficiency transformations. In an exponential decay wave pulse generators such as the ECM 399, ECM 630 and Gemini, the time constant is determined by the values of the resistance and capacitance (RC) settings in the generator. The ECM 399 has fixed RC values which are pre-optimized to provide the standard time constant range of 5 to 6 ms for efficient transformation of gram-negative bacteria and yeast. The ECM 630 and Gemini have adjustable RC settings to span the range of time constants needed for gram-positive bacteria, requiring a range from 5 to 10 ms time constants. Other prokaryotic cell lines need the advantage of adjust able RC values due to the need of even higher ranges of time constants to achieve efficient transformation.
Economical Solution
The ECM 399 provides the voltage range needed to achieve the field strengths of 12 to 25 kV/cm essential for efficient transformation. The fixed internal resistance and capacitance settings which deliver the pre-optimized time constants of 5 to 6 ms in high voltage (HV) is ideal for the transformation of gram-negative bacteria. This system offers the best low cost solution for simple transformation needs.
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Solution
Labs working with a variety of bacterial and yeast strains often need to transfect mammalian cells as well. This requires more flexibility and control over the electrical parameters such as the voltage range and time constant for successful transfection. The ECM 630 and Gemini have been found to be efficient and the best instrument for select mammalian cell lines such as mouse stem cells.
High Throughput (HT) Solution
Not only are the Gemini X2 and the ECM 630 a powerful stand-alone systems for transformation and transfection applications, but they are capable of supporting a high throughput (HT) plate handler. The HT plate handler is an accessory which easily connects to the Gemini X2 or ECM 630 for delivery of the powerful exponential wave pulse to electroporate 25- or 96-well electroporation plates in seconds. The HT multi-well system is an effective and affordable tool for optimizing electrical or biological parameters quickly and simply.
Typical Results
References
Cashmore, TJ, et al. Identification of a Membrane Protein Required for Lipomannan Maturation and Lipoarabinomannan Synthesis in Corynebacterineae. J. Biol. Chem. 2017; jbc-M116.
Lee JH, Park SW, Kim YM, Oh JI. Functional Characterization of the CutI Gene for the Transcription of Carbon Monoxide Dehydrogenase Genes in Mycobacterium Sp. Strain JC1 DSM 3803. J Microbiol. 2017;55: 31-36.
Weger-Lucarelli, J, et al. Development and Characterization of Recombinant Virus Generated from a New World Zika Virus Infectious Clone. J. Virol. 2017 Oct;91(19): e01765-16.
Bakhshi PK, et al. Manufacturing Man-Made Magnetosomes: High-Throughput In Situ Synthesis of Biomimetic Magnetite Loaded Nanovesicles. Macromol Biosci. 2016;16: 1555-1561.
Kim, SJ, Ohgew K, Cerniglia, CE. Phenotype-Based Identification of Key Enzymes for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH) Metabolism from Mycobacteria Using Transposon Mutagenesis and a PAH Spray Plate.In: McGenity T., Timmis K., Nogales B. (eds). Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology Protocols. Springer Protocols Handbooks. 2015. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. 161-175.
Lee J, Jang YS, Papoutsakis ET, Lee SY. Stable and Enhanced Gene Expression in Clostridium Acetobutylicum using Synthetic Untranslated Regions with a Stem-Loop. J Biotech. 2016;230: 40-43.
Lin TL, Pan YJ, Hsieh PF, Hsu CR, Wu MC, Wang JT. Imipenem Represses CRISPR-Cas Interference of DNA Acquisition through H-NS Stimulation in Klebsiella Pneumoniae. Sci Rep. 2016;17: 21644.
Oakes BL, et al. Profiling of Engineering Hotspots Identifies an Allosteric CRISPR-Cas9 Switch. Nat Biotechnol. 2016; 34: 646-651.
Rojas-Sánchez S, et al. Transcription of Leishmania major U2 small nuclear RNA gene is directed by extragenic sequences located within a tRNA-like and a tRNA-Ala gene. Parasite Vector. 2016; 9: 401.
Wisniewski JA, et al. TcpM: a novel relaxase that mediates transfer of large conjugative plasmids from Clostridium perfringens. Mol. Microbiol. 2016 Mar;99(5): 884-96.
Dobroff AS, et al. Ligand-Directed Profiling of Organelles with Internalizing Phage Libraries. Curr Protoc Protein Sci. 2015;79: 30.4.1-30.4.30.
Jones SC, Price CT, Santic M, Abu Kwaik Y. Selective Requirement of the Shikimate Pathway of Legionella pneumophila for Intravacuolar Growth within Human Macrophages but not within Acanthamoeba. Infect Immun. 2015;83: 2487-2495.
Kim S, et al. Redox-Switch Regulatory Mechanism of Thiolase from Clostridium acetobutylicum. Nat Commun. 2015;22 8410.
Knut M, Tolstorukov I, Cregg J. Electroporation of Pichia pastoris. In: van den Berg M., Maruthachalam K. (eds) Genetic Transformation Systems in Fungi, Volume 1. Fungal Biology. 2015.Springer, Cham 87-91.
Ren J, et al. Acetylation Regulates Survival of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium under Acid Stress. Appl Environ Microb. 2015;81(17): 5675-5682.
Wisniewski JA, Teng WL, Bannam TL, Rood JI. Two Novel Membrane Proteins, TcpD and TcpE, Are Essential for Conjugative Transfer of pCW3 in Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 2015;197: 774-781.
Cameron DE, Collins JJ. Tunable Protein Degradation in Bacteria. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32: 1276-1281.
Ravi Kant H, Balamurali M, Meenakshisundaram S. Enhancing precursors availability in Pichia pastoris for the overproduction of S-adenosyl-lmethionine employing molecular strategies with process tuning. J. Biotech. 2014;188: 112-121.
Nováková J, et al. Improved method for high-efficiency electrotransformation of Escherichia coli with the large BAC plasmids. Folia Microbiol. 2014;59(1): 53-61.
Ueno Y, Hoshinoo K, Tagawa Y. Mutations in the major outer membrane protein gene from Histophilus somni by an allelic exchange method. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2014;106: 83-92.
Wang L, et al. A new strategy for secretory expression and mixed fermentation of recombinant human collagen a1 (III) chain in Pichia pastoris. Biotech. Bioproc. Eng. 2014;19(5)5: 916-924.
Wei Y, Hu H, Lun ZR, Li Z. Centrin3 in Trypanosomes Maintains the Stability of a Flagellar Inner-Arm Dynein for Cell Motility. Nat Comms. 2014;5: 4060.
Plants & Insects
For many years, Agriculture and Horticulture labs have used electroporation to transform plants in order to generate transgenic crops (GMO). Electroporation offers a an alternative method for the delivery of genes directly into plant cells, plant tissues and plant protoplasts. Electrofusion allows for the fusion of plant protoplasts for transgenic modified plant applications. Transformation of plants can be successfully accomplished without prior removal of the cell wall, allowing for greater genetic manipulation potential of the plant cells. Whether performing a stable transformation to generate crops with better traits, enhance productivity or developing transient transformations for gene expression, electroporation has obtained high efficiencies and cell viabilities. BTX offers protocols for successful transformations of many plant cell lines such as rice, sweet potatoes, wheat, barley, tobacco leaf, cotton and root protoplasts using the ECM 630, ECM 830 and ECM 2001.
There are few techniques available that are powerful enough to transfect insect cells and tissues. Electroporation is one of those methods. It has been widely used for successfully transecting insect cells, such as Drosophila, Bombyx mori embryos and larval tissues. Using electroporation on insect cells has proven extremely useful for invertebrate genetic manipulation and genome function analysis.
Plants
Electroporation offers an alternative method for the delivery of genes directly into plant cells with out prior removal of the cell walls allowing for greater genetic manipulation potential of plant cells. The stable or transient integration of genes into plant protoplast cells is efficiently performed with high cell viability using the ECM 830 square wave system. It has been reported that wheat, barley leaf, and root protoplasts have been successfully transformed and electroporation parameters optimized using the BTX line of generators. The BTX ECM 630 exponential decay wave system provides a wide scope of voltage settings (10-2500V) resulting in field strengths up to 25kV/cm and an array of possible time constants (pulse durations) critical for highly efficient electro-transformations. The ECM 630 system enables transformation of Agrobacterium for gene transfer with efficiencies of 1x108 transformants/ug DNA.
Field Strengths and Time Constants
The ECM 630 exponential decay wave pulse generator has the voltage range needed to reach the high field strengths (kV/cm) these cells require. The adjustable resistance and capacitance combinations create a wide range of time constant options to ensure efficient transformations of difficult cell types including plant tissues and Agrobacterium cells producing efficiencies of 1 x 108 pfu/ugs.
Powerful Exponential Decay Wave Pulse
The diverse combination of settings joined with the power of the exponential decay wave pulse generator provides the permeation of cell membrane for efficient transformation of Drosophila, SF9 cells, and many other insect cells.
Square Wave Gentle Strength
Transformation of plant protoplasts, insect embryos and various tissues including delicate brain tissues require the gentle strength of the square wave pulse generator, the ECM 830. The square wave pulse generator provides the voltage ranges and multiple pulsing capabilities needed for efficient membrane permeation with out sacrificing cell viability critical to these applications.
Protoplast Fusion
Plant protoplast fusion is used to generate genetically modified hybrids to improve traits or enhance production. The use of electrofusion allows for fusion of plant protoplast and the transfer of genes more effectively compared to standard cDNA transformations. The ECM 2001 system is a multi-purpose system for both electrofusion and electroporation. It employs both AC and DC wave forms to align cells for better membrane contact, fuses cells together and with post AC alignment continues to maintain compression of cells during the rounding off period. The span of voltages, pulse lengths and multiple pulsing up to 9 pulses, allow this system to function solely as an electroporator for plant protoplast and mammalian cell transfections.
Insects
Electroporation has been widely used for successfully transfecting insect cells and tissues. Jean-Luc Thomas et al. 2003, found that working with a BTX ECM 830 square wave generator to transfect Bombyx mori embryos and larval tissue was efficient, simple and reliable. The BTX generators can be used with our specialty electrodes for tissue specific transfection in insects or BTX microslides can be utilized for the transformation of large numbers of insect eggs.
References
Ravinder Kaur Grewal, Monika Lulsdorf, Janine Croser, Sergio Ochatt, Albert Vanderberg, Thoma D. Warkentin,. Doubled-haploid Production in Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): Role of Stress Treatments. Plant Cell Reports, 30, May, 2009
S. Ochatt, C. Pech, R. Grewal, C. Conreux, M. Lulsdorf, L. Jacas,. Abiotic Stress Enhances Androgenesis from Isolated Microspores of Some Legume Species. Journal of Plant Physiology, Vol 166:1229-1346, 2009
Luc F.M. Rouws, Jean L. Simoes-Araujo, Adriana S. Hernerly, Jose I. Baldani,.Validation of a Tn5 Transposon Mutagenesis System for Gluconactobacter diazotrophicus Through Characterization of a Flagellar Mutant. Arch Micorbiol 189:397-405, 2008
Kyle Golden, Veena Sagi, Nathan Markwarth, Bin Chen and Antonia Moterio,. In Vivo Electroporation of DNA Into the Wing Epidermis of the Butterfly, Bicyclus aynana. Journal of Insect Science 7:53, 2007
T.M. GE, X.H. Lin, F.L. Qin, S.W. Yu and Y.J. Yu,. Protoplast Electroporation Between Common Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Italian Ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam) and Regeneration of Mature Cybrids. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol –Plant 42:179-187, 2006
Yijun Qi, Zuehua Zhong, Asuka Itaya and Biao Ding,. Dissecting RNA Silencing in Protoplasts Uncovers Novel Effects of Viral Supressors on the Silencing Pathway at the Cellular Level. Nucleic Acids Research Vol. 32 No 22, 2004
John J. Weiland,. Transformation of Pytheium aphanidermantum to Geneticin Resistance. Curr Genet 42:344-352, 2003
Jean-Luc Thomas. Electroporation, an Alternative to Biolistics for Transfection of Bombyx mori Embryos and Larval Tissues. Journal of Insect Science, 3:17. June, 2003
Mammalian Cell Transfections
Electroporation is an efficient non-viral method used to transfect genes and other molecules into mammalian cell lines. This technology is commonly used to study gene targeting, function and to understand protein regulation. Electroporation is a standard method used to transfect mammalian cell lines to express recombinant human proteins which are used for therapeutic purposes. Gene delivery by this method is typically used to create a transient transfection in order to study protein expression or to temporarily knockout or “silence” these genes using siRNA; which is used to study gene targeting and function. Alternatively the stable transfection integrates the gene into the genome of the cell for long term expression of a human protein. The use of the BTX square wave pulse generator ECM 830 offers the control needed to adjust electrical settings for optimization of parameters. This system is powerful enough to yield high transfection efficiencies for cell lines and difficult to transfect cell types including stem cells and primary cells. The gentle square wave pulse allows for high cell viability of these cell types.
Mammalian Cell Transfections – “The Advantage”
The advantage of the square wave lies in its superior ability to introduce genes, proteins and other molecules into mammalian cells efficiently. Mammalian cells respond exceptionally better to the gentle strength of the square wave pulse to allow for both high transfection efficiencies while maintaining cell viability. With the ECM 830, users have control over their parameters, including voltage, pulse length, number of pulses and pulse intervals for more accurate optimization of conditions. BTX developed a system that provides the versatility a researcher needs to transfect single samples in cuvettes or scale up to 96 wells quickly and simply with the addition of a High Throughput plate handler for 96 and 25 well electroporation. Other transfection applications include in vivo, in utero, ex vivo tissues and in ovo transfections using our array of specialty electrodes from BTX.
Wide Voltage and Pulse Length Range
With the ability to achieve a wide range of field strengths with voltage settings up to 3000 V and pulse lengths as low as 10 µs, the researcher can set parameters to allow for molecules of various sizes to be delivered into the cells efficiently while maintaining high cell viability.
Multiple Pulsing
Many cell types can be difficult to transfect due to the delicate nature of the cell line. Multiple pulsing and the ability to set intervals between pulses allow cells the opportunity to recover between pulses resulting in higher cell viability and efficient transfections.
High Throughput (HT)
The ECM 830 can be coupled with our specially designed HT plate handler, which can transfect up to 96 or 25 well samples quickly and efficiently. This greatly reduces the time to optimize experiments and process large number of samples.
Gene Silencing
The use of siRNA to analyze gene function is fundamental for research. The ECM 830 has been used successfully for this application with inhibition and cell viabilities of up to 90%. It has been reported recently that single cell expression of miRNA in a mouse brain was successfully achieved with the ECM 830.
BTXpress™ High Performance Electroporation Solution
A single buffer developed to quickly and efficiently deliver genes into mammalian cells that were previously recalcitrant to chemical and non-viral methods. BTXpress™ supports high efficiency transfection in numerous cell types while maintaining critical cell viability. This high performance electroporation buffer is equally effective at delivering DNA as well as siRNA into mammalian cells. This buffer is not restricted to use in just BTX electroporation systems. As a universal solution, the BTXpress™ electroporation buffer can be used in other systems including the Amaxa™ Nucleofector™, achieving similar results. The BTXpress™ High Performance Electroporation Solution is offered as a kit including the BTX plus cuvettes with transfer pipette or as a buffer alone.
References
GE Davies, SM Locke, PW Wright, H Li, RJ Hanson, JS Miller, and SK Anderson; Identification of Bidirectional Promoters in the Human KIR Genes. Genes and Immunity 8, 245-253, 2008
Ken Nguyen, Nicholas R. Sylvain, and Stephen C. Bunnell. T Cell Costimulation via the Integrin VLA-4 Inhibits the Actin-Dependent Centralization of signaling Microclusters Containing the Adaptor SLP-76., Immunity 28, 810-821, June 2008
Ami A. Deora, Fernando Diaz, Ryan Schreiner and Enrique Rodreguez-Boulan; Efficient Electroporation of DNA and Protein into Confluent and Differentiated Epithelial Cells in Culture. Traffic 8:1304-1312, 2007
Stephen C. Bunnell, Andrew L. Singer, David I. Hong, Berri H. Jacque, Martha S. Jordan, Maria-Cristina Seminario, Valarie A. Barr, Gary A Koretzky and Lawrence e. Samelson. Persistence of Cooperatively Stabilized Signaling Clusters Drives T-Cell Activation. Molecular and Cellular Biology, P.7155-7166, Oct 2006
Yangbing Zhao, Zhili Zheng, Cyrille J. Cohen, Luca Gattinoni, Douglas C. Plamer, Nicholas P. Restifo, Steven A. Rosenberg, and Richard A. Morgan. High-efficiency transfection of primary human and mouse T lymphocytes using RNA electroporation. Molecular Therapy 13, 151-159 2006
William J. Buchser, Jose R. Pardinas, Yan Shi, John L. Bixby, and Vance P. Lemmon. 96-Well Electroporation Method for Transfection of Mammalian Central Neurons. BioTechniques Vol. 41, No. 5, 2006
Diana A. Stavreva, Miyuki Kawasaki, Miroslav Dundr, Karel Koberna, Waltraud G. Muller, Teruko Tsujimura-Takahashi, Wataru Komatsu, Toshiya Hayano, Toshiaki Isobe, Ivan Raska, Tom Misteli, Nobuhiro Takahashi, and James G McNally, Potential Roles for Ubiquitin and the Proteasome during Ribosome Biogenesis, Molecular and Cellular Biology, P 5131-5145, July 2006
Silvija Jarnjak-Jankovic, Rolf D Pettersen, Stein Saeboe-Larssen, Finn Wesenberg and Gustav Gaudernack. Evaluation of dendritic cells loaded with apoptotic cancer cells or expressing tumor mRNA as potential cancer vaccines against leukemia, BMC Cancer 5:20, 2005
Jonathan M. Dermott, J. M. Gooya, B. Asefa, S. R. Weiler, M. Smith, J. R. Keller; Inhibition of Growth by p205: A Nuclear Protein and Putative Tumor Suppressor Expressed During Myeloid Cell Differentiation. Stem Cells 22:832-848, 2004
Smita Nair, David Boczkowski, Benjamin Moeller, Mark Dwhirst, Johannes Vieweg and Eli Gilboa; Synergy Between Tumor Immunotherapy and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. Blood Journal, 2003
Please note: Amaxa™ Nucleofector™ are a registered trademarks.
In Vivo, In Utero & In Ovo Applications
The delivery of genes and drugs directly into living tissues has significant implications in gene therapy applications, cancer treatments, vaccine development and transgenic animal production. Tissues and whole embryos can be transfected with the use of specialty electrodes for the following methods; in vivo, in ovo, in utero and ex vivo tissues. Electroporation-mediated gene and drug delivery have been shown to substantially increase intracellular uptake and expression of DNA, siRNA and miRNA in a variety of tissue such as muscle, skin, liver, retina, testis and kidney.
The use of our square wave technology provides the gentle power needed to efficiently deliver the genes and molecules to the various tissues while still maintaining the viability critical for the survival of tissue. Other more delicate in vivo tissues that are successfully electroporated include in utero embryos, brain tissue in both embryo and adult animal as well as marine species such as zebrafish.
In Vivo
BTX offers researchers a wide selection of specialty electrodes to deliver molecules such as DNA, siRNA, miRNA and various drugs into tissues of living animals. This technique is a valuable tool which assists in the evaluation of a gene function and cell development. Depending on the research application, BTX offers both invasive and non-invasive electrodes. BTX provides the tools for efficient, easy and reproducible transfections into specific tissues, embryos and ex vivo samples.
In Utero
Tweezertrodes™ and Genepaddles™ are ideally shaped to electroporate into rat or mouse embryos allowing the user to study the postulated roles that genes play during embryonic development.
In Ovo
The use of electrodes such as the L-shaped Genetrodes™ have been established as an effective method for introducing molecules such as DNA, siRNA and miRNA into embryos for the study of development, gene function and protein expression.
Oocytes
Studies of gene function through gene silencing is a powerful technique that is not limited to cultured cells. BTX has an entire line of electrodes that make siRNA delivery possible into intact blastocysts. Soares et al. 2005 used BTX ECM 2001 generator and flat electrodes to introduce RNA to study the signaling pathways in the developing mouse embryo.
Zebra Fish
Zebrafish have shown to be a very useful model for studying vertebrate development given the transparency of the fingerlings during early stages of development. Rambabu et al. 2005 used a BTX ECM 830 and Tweezertrodes™ in conjunction with microinjection of naked DNA to study the effect of electroporation as a method for gene delivery into adult zebrafish.
Mouse Embryonic Brain
With the help of BTX electroporation generators Tonelli et al. 2007 were able to transfect a dual-fluorescence reporter/sensor plasmid into the mouse embryonic brain. They developed a technique to detect expression at the single cell level making it possible to monitor miRNA appearance and disappearance in defined cell lineages during vertebrate development.
Transgenic Animal Development
Development of transgenic animals using standard methods is highly time consuming and is costly. With the help of BTX square wave
electroporation Majumdar et al. 2008 was able to in vivo transfection to deliver genes directly into undifferentiated germ cells in mouse testis to establish a stably transfected spermatogonial cells. These mice were then mated to wild type females and sired transgenic offspring for up to a year following transfection.
References
Liyun Zheng, Fuyan Wang, Zhongdong Yang, Jianjun Chen, Haiyan Chang and Ze Chen., A single immunization with HA DNA vaccine by electroporation induces early protection against H5N1 avian influenza virus challenge in mice. BMC Infectious Diseases, 9:17, February 2009
Magali Irla, Murelle Saade, Adrien Kissenpfennig, Lionel Franz Poulin, Lee Leserman, Patrice N. Marche, Evelyne Jouin-Marche, Francois Berger, Catherine Nguyen., ZAP-70 Restoration in Mice by In Vivo Thymic Electroporation. PLoS ONE 3(4):e2059. doc10.1371/journal. Pone. 0002059, 2008
Juliana M Sousa-Canavez, Flavio C Canavez, Katia RM leite, And Luiz Ha Camara-Lopes., Therapeutic dendritic cell vaccine preparation using tumor RNA transfection: A promising approach for the treatment of prostate cancer. Genetic Vaccines and Therapy, 6:2 2008
Tracy L Young-Pearse, Allen C Chen, Rui Chang, Cesar Marquez and Dennis J Selkoe., Secreted APP regulates the function of full-length APP in neurite out growth through interaction with integrin beta I. Neural Development, 3:15, 2008
Lisa Marie Langevin, Pierre Mattar, Raffaella Scardigli, Myriam Roussigne, Cairine Logan, Patrick Blader, and Carol Schuurmans., Validating In Utero electroporation for the rapid analysis of gene regulatory elements in the Murine Telencephalon. Developmental Dynamics 236:1273-1286, 2007
Shin Onodera, Shigeki Ohshima, harukazu Tohyama, Kazunori Yasuda, Jun Nishihira, Yoichiro Iwakura, Ikkei Matsuda, Akio Minami and Yoshikazu Koyama., A Novel DNA Vaccine Targeting Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Protects Joints From inflammation and Destruction in Murine Models of Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism Vol.56, No. 2, pp 521-530, February 2007
Davide De Pietri Tonelli, Federico Calegari, Ji-Feng Fei, Tadashi Nomura, Noriko Osumi, Carl-Philipp Heisenberg, and Wieland B. Huttner. Single-Cell Detection of microRNAs in Developing Vertebrate Embryos After Acute Administration of a Dual-Fluorescence Reporter/Sensor Plasmid. BioTechniques 41:727-732, December 2006
Christophe E Pierreux, Aurélie V Poll, Patrick Jacquemin, Frédéric P Lemaigre, Guy G Rousseau. Gene Transfer into Mouse Prepancreatic Endoderm by Whole Embryo Electroporation. JOP.J Pancreas 6(2):128-135, 2005
K. Murali Rambabu, S. H. Narayana Rao and N Madhusudhana Rao. Efficient Expression of Transgenes in Adult Zebrafish by Electroporation. BMC Biotechnology, 5:29, 2005
Miguel L. Soares, et al. Functional Studies of Signaling Pathways in Peri-Implantation Development of the Mouse Embryo by RNAi. BMC Developmental Biology, 5:28, 2005
3. Electroporation Guides
- BTX Electroporation Systems Crossover Guide
BTX generally recommends a square waveform for mammalian cell work, and an exponential decay waveform for bacteria and yeast applications. However, there are some exceptions and crossover in the use of our electroporation generators. - Electroporation Decision Guide
This guide will help you choose the right system ans electrode for your application. - Electroporation Definitions Guide
A glossary of common electroporation terms. - General Electroporation Optimization Guide
An overview of key elements for effective transformation.
4. BTX Electroporation Systems
Gemini
Our most flexible and universal electroporation instrument containing twin wave electroporators for both square wave and exponential decay wave electroporation in a single unit. These waveform combinations enable researchers to easily and efficiently electroporate eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells in cuvettes or plates with one easy-to-use setup. Also compatible with additional applications such as in vivo, in ovo and adherent cell electroporation. Comes with pre-set protocols for the most common eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell types, as well as CRISPR applications. More information about the Gemini.
ECM® 830
This square wave electroporation system is engineered mainly for mammalian cell transfections (in vivo, ex vivo, in ovo tissue and ex plant) as well as for nuclear transfer and CRISPR applications.The 830 is also capable of performing certain cell fusion applications which will require the use of a manual cell alignment method. It is ideal for gene, drug and protein delivery studies. Bacterial transformation of bacteria to generate plasmids can be accomplished but at lower efficiencies than with our ECM 630 decay wave system. More information about the ECM 830.
ECM® 630
This exponential decay wave pulse generator is primarily used for bacteria and yeast transformation applications. It can be used for efficient transfection of mammalian cells but much lower cell viabilities compared to the ECM 830 square wave pulse system, with the exception of mouse embryonic stem cells. More information about the ECM 630.
ECM® 399
This exponential decay wave generator is our most economical unit for a lab doing mainly gram (-) bacteria and yeast applications. This unit is not recommended for mammalian transfection. More information about the ECM 399.
ECM® 2001
This square wave pulse electroporator and electrofusion generator is primarily used for cell fusion work and mammalian cell transfection. It can also be used for transforming bacteria, but with lower efficiencies than with an exponential decay waveform. More information about the ECM 2001.
AgilePulse
A waveform electroporation solution providing maximum efficiency DNA delivery for vaccine development. Large volume option for fast, efficient transfection of up to 10 mL cell suspension. More information about the AgilePulse.
5. Electroporation Papers Bibliography
In vitro Electroporation
Kim, T. et. al., Mesoporous Silica-Coated Hollow Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles as Positive T1 Contrast Agents for Labeling and MRI Tracking of Adipose- Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 133, 2955–2961, 2011
Kataoka, N. et. al., Development of butanol-tolerant Bacillus subtilis strain GRSW2-B1 as a potential bioproduction, AMB Express, 1:10, 2011
Hutson, T.H. et. al., Optimization of a 96 well electroporation assay for post natal rat CNS neurons suitable for cost–effective medium-throughput screening of genes that promote neurite outgrowth. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience; 4(55): December 2011
Djouad, F. et. al., Activin A expression regulates multipotency of mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res & Therapy, 1(11), 2010
Sankaranarayanan , K. et. al., Electro-Molecular Therapy using Adult Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Proc. ESA Annual Meeting on Electrostatics, 13, 2010
Blackmore, M. et. al., High content screening of cortical neurons identifies novel regulators of axon growth. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience, 44, 43 -54, 2010
Yao, S. et. al., Improvement of electroporation to deliver plasmid DNA into dental follicle cells. Biotechnol J. October ; 4(10): 1488–1496. 2009
Rinaldi, G., Development of Functional Genomic Tools in Trematodes: RNA Interference and Luciferase Reporter Gene Activity in Fasciola hepatica. PLoS One, 2(7); e260, July 2008
Nguyen, K. et al., T Cell Costimulation via the Integrin VLA-4 Inhibits the Actin-Dependent Centralization of Signaling Microclusters Containing the Adaptor SLP-76. Immunity, 28, 810–821, June 2008
Yang, C. et al., Dimeric heat shock protein 40 binds radial spokes for generating coupled power strokes and recovery strokes of 9 + 2 flagella. The Journal of Cell Biology, 180(2), pp. 403-415, January 28, 2008
Zhao, Y. et al., High-Efficiency Transfection of Primary Human and Mouse T Lymphocytes Using RNA Electroporation. Molecular Therapy, Vo. 13, No. 1, January 2006
Heaney, J.D. et. al. Tissue-specific expression of a BAC transgene targeted to the Hprt locus in mouse embryonic stem cells. Genomics, 2004
Raoul, C. et al., Motoneuron Death Triggered by a Specific Pathway Downstream of Fas: Potentiation by ALS-Linked SOD1 Mutations. Neuron, Vol. 35, 1067-1083, September 12, 2002
Dawson, K. et al., Insulin-Regulated Trafficking of Dual-Labeled Glucose Transporter 4 in Primary Rat Adipose Cells, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 287, pp. 445–454, 2001
In vivo Electroporation
Johannson, D. et. al., Intradermal Electroporation of Naked Replicon RNA Elicits Strong Immune Responses. PLoS ONE, 7(1): e29732, 2012
Daftarian, P. et. al., In vivo Electroporation and Non-protein Based Screening Assays to Identify Antibodies Against Native Protein Conformations. Hybridoma, 30(5); 2011
Hallengard, D. et. al., Comparison of plasmid vaccine immunization schedules using intradermal in vivo electroporation. Clinical Vaccine Immunology, 2011
Bolhassani, A. et. al., Improvement of different vaccine delivery systems for cancer therapy. Molecular Cancer, 10(3), 2011
Li, W. et. al., The Effects of Irreversible Electroporation (IRE) on Nerves. PLoS ONE, 6(4), 2011
Lladser, A. et. al., Intradermal DNA electroporation induces survivin-specific CTLs, suppresses angiogenesis and confers protection against mouse melanoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother, 59; 81-92, 2010
Shi, W. et al., Generation of sp3111 transgenic RNAi mice via permanent integration of small hairpin RNAs in repopulating spermatogonial cells in vivo. Acta Biochim Biophy Sci, 42(2): p 116, 2010
Haller, BK. et. al., Therapeutic efficacy of a DNA vaccine targeting the endothelial tip cell antigen delta-like ligand 4 in mammary carcinoma. Oncogene, 29, 4276-4286, 2010
Guo, Y. et. al., Irreversible Electroporation Therapy in the Liver: Longitudinal Efficacy Studies in a Rat Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Research; 70(4) February 15, 2010
Roos, A. K. ,Skin Electroporation: Effects on Transgene Expression, DNA Persistence and Local Tissue Environment. PLoS ONE, 4(9) e7226, 2009
Brave, A. et. al., Late administration of plasmid DNA by intradermal electroporation efficiently boosts DNA-primed T and B cell responses to carcinoembryonic antigen. Vaccine, 27, 3692-3696, 2009
Roos, A. K. et. al., Optimization of Skin Electroporation in Mice to Increase Tolerability of DNA Vaccine Delivery to Patients. Molecular Therapy, 17(9), 1637-1642, Sep 2009
Danner, S. et. al., Seminiferous tubule transfection in vitro to define post-meiotic gene regulation. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, 7(67), 2009
Benton, C. et al., Modest PGC-1_ Overexpression in Muscle in Vivo Is Sufficient to Increase Insulin Sensitivity and Palmitate Oxidation in Subsarcolemmal, Not Intermyofibrillar, Mitochondria*. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283(7); pp. 4228–4240, February 15, 2008
Chesler, A. T., Selective Gene Expression by Postnatal Electroporation during Olfactory Interneuron Neurogenesis. PLoS ONE, 3(1): e1517, 2008
Rao, N. M. et al., Electroporation of Adult Zebrafish. S. Li (ed.), Electroporation Protocols: Preclinical and Clinical Gene Medicine. Methods in Molecular Biology, Vol. 423. p 289, 2008
Johnson, C. J. et al., Technical Brief: Subretinal injection and electroporation into adult mouse eyes. Molecular Vision, 14:2211-2226, 2008
Heller, L. et. al., Comparison of electrically mediated and liposome-complexedplasmid DNA delivery to the skin. Genetic Vaccines and Therapy, 6(16), 2008
Roos, A.K., et. al., Enhancement of Cellular Immune Response to a Prostate Cancer DNA Vaccine by Intradermal Electroporation. Molecular Therapy, 13(2), February 2006
Kong, X. C. et al., Inhibition of synapse assembly in mammalian muscle in vivo by RNA interference. EMBO Rep, 5(2): 183-188, January 2004
Pringle, I. A. et al., Duration of reporter gene expression from naled pDNA in the mouse lung following direct electroporation and development or wire electrodes for sheep lung electroporation studies. Molecular Therapy, 9, S56–S56, 2004
Mikata, K. et al., Inhibition of Growth of Human Prostate Cancer Xenograft by Transfection of p53 Gene: Gene Transfer by Electroporation. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics, Vol. 1, 247–252, February 2002
Pekarik, V. et al., Screening for gene function in chicken embryo using RNAi and electroporation. Nature Biotechnology, 21: 93-96, December 2002
Dujardin, N. et. al., In vivo assessment of skin electroporation using square wave pulses. J Controlled Release, 79, 219-227; 2002
Drabick, J.J. et. al., Cutaneous Transfection and Immune Responses to Intradermal Nucleic Acid Vaccination Are Significantly Enhanced by in Vivo Electropermeabilization. Molecular Therapy, 3(2), Feb 2001
In Utero Electroporation
Maiorano, N. A., et al., Promotion of embryonic cortico-cerebral neuronogenesis by miR-124. Neural Development, 4:40, 2009
Ex Vivo Electroporation
Deora, A.A. et. al., Efficient Electroporation of DNA and Protein into Confluent and Differentiated Epithelial Cells in Culture. Traffic, 8: 1304-1312, 2007
Thomas J-L. et. al., Electroporation, an alternative to biolostics for transfection of Bombyx mori embryos and larval tissues. Journal of Insect Science, 3:17, 2003
Electrofusion
Hwang, K.K. et. al., Enhanced outgrowth of EBV-transformed chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells mediated by coculture with macrophage feeder cells. Immunobiology, 119(7), February 2012
O’Shannessy, D. J. et. al., Characterization of the Human Folate Receptor Alpha Via Novel Antibody-Based Probes. Oncotarget; 2, 1227-1243, 2011
Drozdowski, B. et. al., Generation and characterization of high affinity human monoclonal antibodies that neutralize staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Immune Based Therapies & Vaccines, 8:9, 2010
Ellsworth, J.L. et. al., Recombinant Soluble Human Fc_R1A (CD64A) Reduces Inflammation in Murine Collagen-Induced Arthritis, The Journal of Immunology, 182: 7272–7279, 2009
Shi, L.H. et. al., Trichostatin A and nuclear reprogramming of cloned rabbit embryos. J Anim Sci, 86, 1106-113, 2008
Yu, X. et. al., An optimized electrofusion-based protocol for generating virus specific human monoclonal antibodies, J Immunol Methods, 336(2): 142–151, July 31, 2008
Lee, R. et. al., A High-Throughput Hybridoma Selection Method Using Fluorometric Microvolume Assay Technology. J Biomolecular Screening, 13(3); 2008
Li, J. et. al., Human antibodies for immunotherapy development generated via a human B cell hybridoma technology. PNAS, 103(10): 3557-3562, March 7, 2006
Trevor, K.T. et. al., Generation of dendritic cell–tumor cell hybrids by electrofusion for clinical vaccine application. Cancer Immunology, 2004
Kreutz, F. T. et al., A New Method to Generate Quadromas by Electrofusion and FACS Sorting. Hybridoma, 17(3), 1998
Microinjection
Wang, W. et al., A Fully Automated Robotic System for Microinjection of Zebrafish Embryos. PLoS ONE 2(9):e862, 2007



 800-272-2775
800-272-2775
