
There are several common causes of high cellular toxicity following electroporation. Here’s a list of the top causes of cell death during electroporation and recommended solutions.
Read MoreWelcome To BTX Online ! 

There are several common causes of high cellular toxicity following electroporation. Here’s a list of the top causes of cell death during electroporation and recommended solutions.
Read MoreThe CRISPR/Cas system is a prokaryotic immune system that allows the cell to protect itself from foreign DNA such as a virus or plasmid. Modified versions of CRISPR/Cas9 are being utilized as gene editing tools in revolutionary ways in science and medicine.
Here we explore the formats that CRISPR/Cas9 tools and the benefits of using electroporation to deliver CRISPR gene editing constructs.
Read More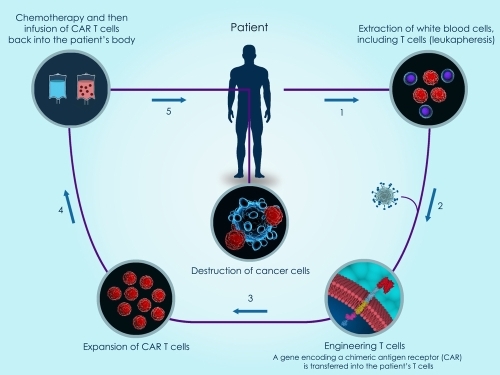
The Immune system is the body’s defense against infections and cancer. It consists of billions of cells that are divided into several different types. A subtype of white blood cells calls Lymphocytes comprise a major portion of the immune system. There are three types: B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes and Natural Killer (NK). In today’s blog post we focus on T lymphocytes (T cells) and how they work to kill tumors.
Read More
Electroporators can come in multiple electrical waveform styles and typically allow you to vary the characteristics of the electrical pulse settings. Every cell type is unique in terms of which pulse characteristics work best. Field Strength (€, usually expressed in V/cm) is dependent on the pulse parameters applied (voltage, capacitance and resistance) and the distance between the electrode or cuvette contacts. Application of this electrical field causes Electropermeabilization (transient pores in the cell membrane through induction of transmembrane voltage) allowing nucleic acids to pass through the cell membrane.
Read More
Transfection is simply getting DNA (or other molecules of interest) into a cell, while keeping that cell alive. We can do this in countless methods which are divided into three main categories; Reagent Based, Instrument Based, Biological Based. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages and may be used for transient or stable transfections. Read on as we indulge ourselves into the top methods to see which one suits you best.
Read More